
Environment
Reducing Water Use
Water is an essential resource that is used in our production cycle. Explicitly, we are committed to reducing our absolute and/or per tonne production water consumption by 10% by 2024 (2019 baseline), through developing and promoting solutions that support efficient and responsible water use. Reuse of wastewater, cooling water, and wash-water are the major practices implemented by ADAMA.
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | Target 2024 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water consumption (m3) | 3,616,837 | 3,521,101 | 3,517,081 | 3,631,392 | 3,231,135 | 3,503,711 | 3,580,210 | 3,586,590 | 3,575,850 | 3,222,189 |
* ADAMA Solutions data. The performance of our three Chinese sites is reported separately.
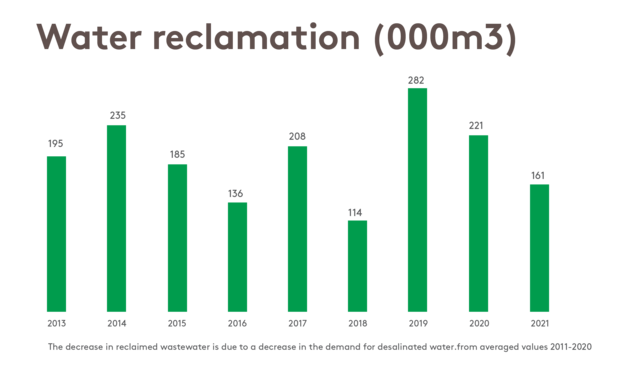
Water Reclamation
Water reclamation projects allow us to reuse wastewater, cooling and wash-water, reducing the environmental impact of discharged water, and saving the consumption of freshwater.
- At the Makhteshim site, we reuse our wastewater following advanced treatment: we operate a reverse osmosis desalination facility to treat our wastewater following a biological wastewater treatment plant (B-WWTP). The reclaimed water is utilized at the major production facility onsite.
- At the Agan, Londrina, and Madrid sites, we reuse wash-water.
- At the Poland site, we recycle cooling water back into the production process.
Reducing Effluent Loads
We aim to keep our surrounding marine and freshwater environments healthy and clean, and so strive to curtail any discharges created at our facilities. Our effluent’s treatment system is a multi-stage process comprises of physical, chemical and biological technologies.
Controlling measures includes online monitoring, composite sampling, and impact assessments. Moreover, at the Agan site, the Israeli Oceanographic and Limnological Research Institute quantify the impact of the effluents, discharged to the Mediterranean Sea, twice a year.
The findings are submitted directly to the Israeli Ministry of Environmental Protection. As of today, no evidence of any impact on marine life and environment has been found.

Case Study
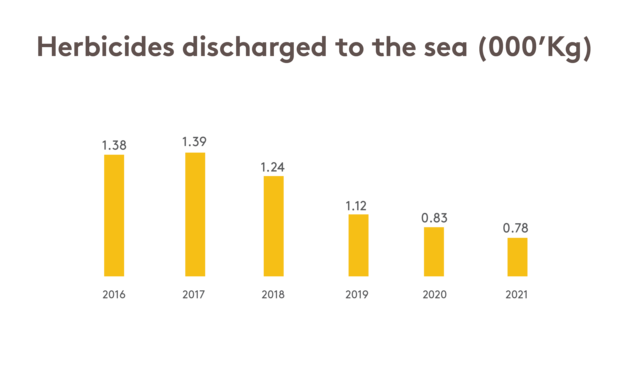
Herbicides at Agan Site
We invest continuous efforts into reducing the residuals of herbicides discharged into the Mediterranean Sea from the Agan site. To that end, we:
- Ensure optimal conditions at our B-WWTP
- Convert liquid waste to solid
- Maintain a high level of housekeeping to eliminate spills
- Despite our increased levels of production, the total amount of discharged herbicides decreased in 44% to 780 Kg within 5 years
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TOC in effluents (tonne) | 302 | 201 | 178 | 208 | 212 | 189 | 181 | 193 |
| Hazardous waste (tonne) | 21,940 | 22,765 | 27,543 | 27,126 | 23,429 | 28,151 | 26,588 | 33,326 |
| Reused or recycle hazardous waste (tonne) | - | - | - | - | - | 2,817 | 8,107 | 7,404 |
ADAMA Agricultural Solutions data. The performance of our three Chinese sites is reported separately
The increase in Hazardous waste is due to increase in production at the sites without an internal wastewater treatment facility.
Reuse and Recycling of Waste
Our production processes generate hazardous and non-hazardous waste that is treated in full compliance with local environmental protection laws. Waste handling is also an important focus for reducing our environmental impact, and to that end we promote diverse initiatives that implement circular economy methodology.

ADAMA promotes recycling, upcycling, and reuse projects to prolong the lifecycle of the materials we use
Case Study
Hazardous waste used as fuel at Agan and MCW BS
During 2021, 4,295 tons of high caloric value hazardous waste was used as fuel substitute to the thermal oxidizers at Agan and MCW NH, saving natural gas.
Sulfuric Acid is Reused to Produce Fertilizer, MCW NH
During 2021, 1,200 tonnes of sulfuric acid, originated from our fungicides production was purified and reused by a fertilizer company to produce phosphorus fertilizer
New Life for Plastic
The Plastic recycling centers at Agan and MCW BS continues to wash and shred empty containers (IBCs, barrels, and jugs). During 2021, the plastic recycling activity was extended by collecting and recycling empty plant protection containers from Israeli farmers. Designated recycle bins (“Green Stations”) were constructed and located at 15 farms, collecting 1-2 tons per month.
Actions to Minimize our Historical Impact
Soil and Groundwater Remediation
We thoroughly monitor and remediate contaminated soil and groundwater in most of our sites. In 2020, we initiated a groundwater and soil gas remediation at one site, finalized a comprehensive soil gas, soil, and groundwater analysis at another site and conducted verification sampling to verify remediation outcome at a third site.

Case Study
Remediating Historic Groundwater Contamination at the Agan Site
During 2021, remediation of contaminated groundwater and soil gas took place at the Agan site. A designated well, located at the center of the plume, extracts the pollutants, which are removed by a treatment system. Remediation is planned to last >10 years, until we meet remediation goals. Simultaneously, remediation of soil gas was implemented using Soil Vapor Extraction technology.


