Septoria Resistance in Wheat
Septoria Fungicide Toolbox
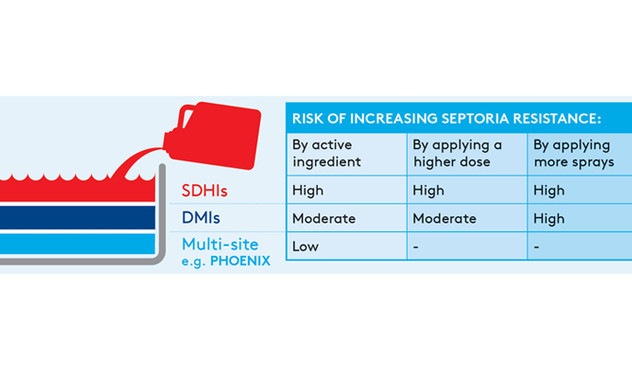
The Septoria fungicide toolbox is limited to three main groups of chemistry: SDHIs, DMIs and multi-site fungicides.
SDHIs
SDHIs (succinate dehydrogenase inhibitors) remain effective against Septoria. They should be used preventatively when disease pressure is low, but disease risk is high. SDHIs offer broad spectrum control of other foliar diseases, but need to be used in moderation to protect them from the increasing threat of resistance.
DMIs
DMIs (DeMethylation Inhibitors) such as BOLIDE®, STELLAR® or PROTHAGO® are an important component in Septoria control and also provide broad spectrum control. Similar to SDHIs, DMIs are single-site chemistries, so protecting DMIs from resistance is key.
Multi-sites
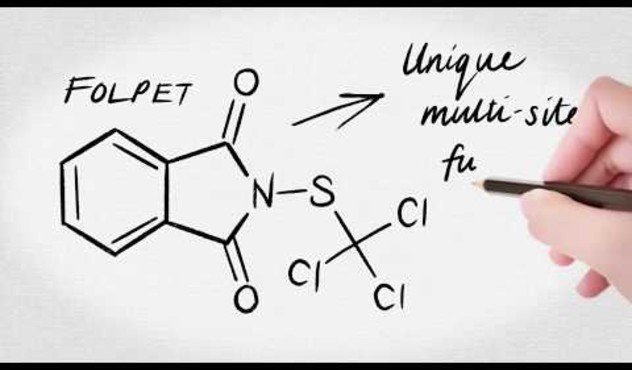
Multi-site fungicide PHOENIX® Fungicide (PHOENIX) is a vital tool in the control and management of Septoria. PHOENIX, containing the active ingredient FOLPET, affects several different metabolic sites within a pathogen and is protectant in action. Folpet has no known resistance and remains at a very low risk of resistance developing in cereal pathogens. In fact, ADAMA’s testing has confirmed no sensitivity shifts against Septoria.
Break the Resistance Cycle with PHOENIX and BOLIDE
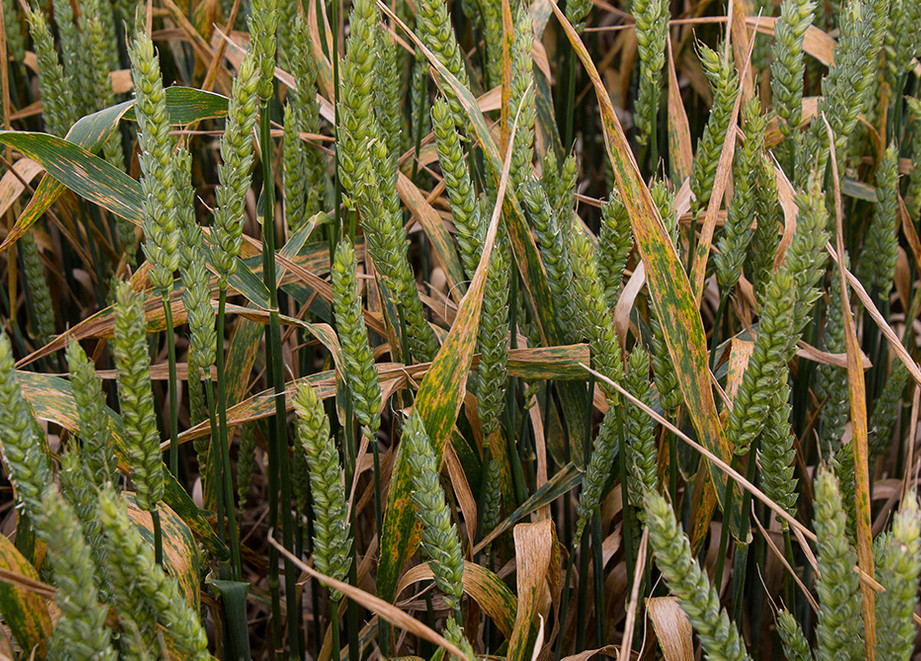
Septoria remains a key issue for New Zealand’s cereal industry. It can have a devastating impact on wheat crops. This is especially the case when Septoria becomes resistant to established fungicide modes of action. It is therefore even more important to practice good resistance management in the field.
Growers know that effective fungicide programmes are critical to the success of any cereal crop. They also know that resistance issues can derail those programmes, allowing Septoria to run riot.
PHOENIX, the proven multi-site protectant and ideal partner for SHDIs and DMIs alike, and BOLIDE, the all-rounder DMI fungicide, are the answer. When combined, they’ll break through the resistance barrier and deliver the ultimate crop protection.
Effective Fungicide Programmes through Multi-Site Activity
Fungicide programmes need to be built from the foundation up with multi-site protectants at the start. Only then can Septoria resistance be managed effectively. Moreover, fungicide programmes need to start early, be well-timed and incorporate robust doses.
Therefore, for your fungicide programme to be successful, you need to take the following into account:
- Always start the mix with a multi-site fungicide in the tank first.
- Maximise the use of multi-site fungicides early in the programme.
- Use robust doses and balanced mixtures
- Limit SDHI dose and number of sprays for effective control
- Use less DMI sprays. Use robust doses in an SDHI mix at key timings instead.
Why PHOENIX is Essential for Your Fungicide Programme
PHOENIX is an innovative cereal fungicide (Phthalimide – Group M4). Folpet, the active ingredient in PHOENIX, works against the disease at a cellular level using a multi-site mode of action. It inhibits both spore germination and cell division and reduces energy production in the mitochondria. Moreover, it is classified as having a “low” resistance risk. In fact, there is no resistance known to folpet globally.

Trial Results
International trials
The effectiveness of multi-site protectants for reducing resistance has been confirmed in research conducted in the UK and Ireland. When mixing PHOENIX with DMIs and SDHIs in field sensitivity trials, there was a reduction in selection pressure compared to straight DMIs or SDHIs.
Overseas modelling further shows that the useful life of high-risk, single-site chemistry like DMIs and SDHIs increases with the addition of multi-site protectants like PHOENIX. This is vitally important as there are a limited number of chemical groups available for controlling Septoria.
New Zealand trials
Extensive research has also been conducted in New Zealand. Results show that adding PHOENIX to commonly used DMIs (STELLAR and Proline®) significantly reduced disease and improved grain yield in sensitive varieties.

Why is Application Timing Critical?
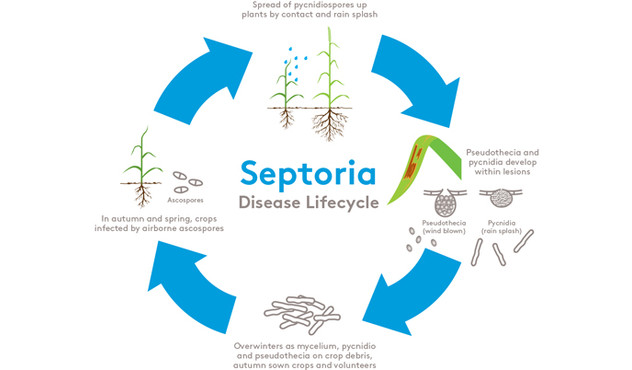
The right application timing is significant for controlling Septoria. Septoria has a very long latent period (14 – 42 days). Crops will be infected long before disease symptoms show.
When to apply? At T1!
The critical timing to apply a multi-site protectant like PHOENIX with a DMI fungicide such as BOLIDE, STELLAR or PROTHAGO is at T1, when leaf 3 emerges. An infected leaf 3 can easily infect leaf 2 and the flag leaf.
Thus, keeping leaf 3 clean is essential for maintaining full yield potential as the crop reaches maturity. This is the time to control Septoria with an effective and adequate fungicide programme. For optimum results though, PHOENIX should be applied at T1 and T2.
PHOENIX is limited to two applications only. For more details on application please read the PHOENIX label.